Can You Use a Leaf Blower with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction? A Comprehensive Guide
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
- 3 The Impact of Leaf Blowers on Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
- 4 Practical Considerations for Using a Leaf Blower with ETD
- 5 Insights and Expert Opinions
- 6 FAQs
- 6.1 1. Can using a leaf blower worsen Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
- 6.2 2. What precautions should I take if I need to use a leaf blower with ETD?
- 6.3 3. Are there quieter alternatives to traditional leaf blowers?
- 6.4 4. How can I manage ETD symptoms when exposed to loud noises?
- 6.5 5. What are some non-mechanical alternatives for yard maintenance?
- 7 Conclusion
Introduction
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) is a common condition that affects many individuals, causing discomfort and impacting quality of life. It can lead to symptoms such as ear fullness, pain, and hearing difficulties. In this article, we will explore a question that may seem peculiar but is of significant concern to those suffering from ETD: “Can you use a leaf blower with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?”
Leaf blowers are powerful tools used for yard maintenance, often generating high levels of noise and strong air currents. Understanding how these factors may interact with ETD is crucial for managing symptoms and making informed decisions about using such equipment. This article will delve into the mechanics of ETD, the impact of leaf blowers on the condition, and offer practical advice for those navigating this intersection.
Understanding Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
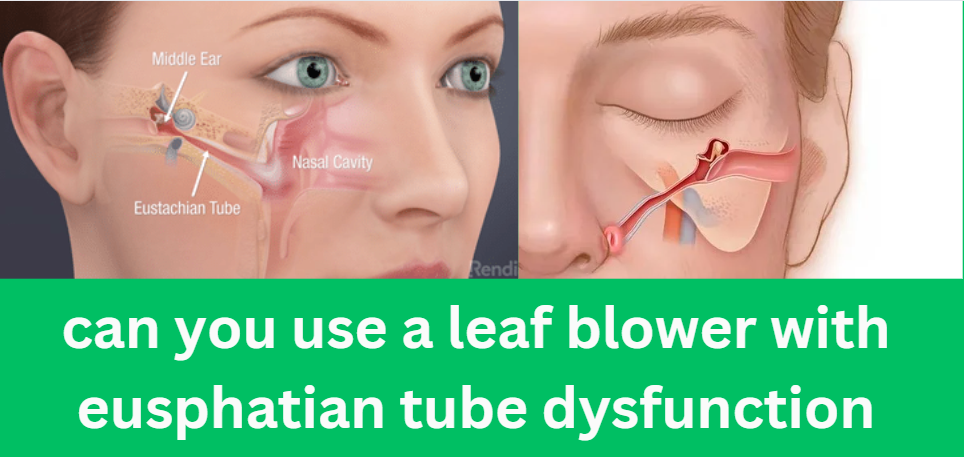
1. What is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction occurs when the Eustachian tube, a small passageway connecting the middle ear to the back of the nose, fails to open or close properly. This dysfunction can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
- Ear Fullness: A sensation of pressure or fullness in the ear.
- Hearing Loss: Difficulty hearing or muffled sounds.
- Ear Pain: Discomfort or pain in the ear.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the ears.
- Balance Issues: Problems with equilibrium or dizziness.
The Eustachian tube’s primary functions are to equalize ear pressure and drain fluids from the middle ear. Dysfunction can be caused by infections, allergies, sinus issues, or anatomical abnormalities.
2. Symptoms and Causes
ETD can arise from various factors, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies can cause inflammation and swelling of the Eustachian tube.
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Colds and sinus infections can block the Eustachian tube.
- Barometric Pressure Changes: Rapid changes in altitude or pressure can affect the tube’s ability to regulate pressure.
- Anatomical Abnormalities: Structural issues may impede the tube’s function.
The Impact of Leaf Blowers on Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
1. Noise Levels and Ear Health
Leaf blowers are known for their high noise levels, often reaching above 100 decibels. Prolonged exposure to such noise can lead to:
- Hearing Damage: Persistent loud noise can damage hearing and exacerbate existing conditions.
- Increased Ear Pressure: The intense noise can contribute to a feeling of ear pressure, which may worsen ETD symptoms.
For individuals with ETD, exposure to loud noises can aggravate the sensation of fullness and discomfort in the ears. It is essential to consider the potential effects of noise when using or being around leaf blowers.
2. Airflow and Pressure Changes
Leaf blowers generate strong air currents, which can create additional pressure around the ears. This might affect ETD in several ways:
- Pressure Fluctuations: The strong air blasts can cause fluctuations in ear pressure, exacerbating ETD symptoms.
- Increased Discomfort: The sensation of strong air currents hitting the ears might increase discomfort and the feeling of fullness.
Practical Considerations for Using a Leaf Blower with ETD
1. Protective Measures
If you have ETD and need to use a leaf blower, consider taking the following precautions:
- Use Ear Protection: Wear earplugs or earmuffs to protect your ears from high noise levels. This can help minimize discomfort and potential damage.
- Minimize Exposure: Limit the duration of use to reduce the risk of exacerbating your symptoms.
- Maintain Distance: Try to keep a safe distance from the blower’s direct airflow to avoid added pressure on your ears.
2. Alternative Options
If using a leaf blower proves too uncomfortable or exacerbates your ETD symptoms, consider alternative yard maintenance options:
- Manual Tools: Use rakes or brooms, which do not produce the high noise levels or strong air currents associated with leaf blowers.
- Quiet Leaf Blowers: Some models are designed to operate more quietly. Explore options that generate less noise and are less likely to affect your ETD.
Insights and Expert Opinions
1. Medical Perspective
From a medical standpoint, it is essential for individuals with ETD to manage their symptoms carefully, particularly when exposed to environmental factors that may worsen their condition. Experts recommend:
- Consulting with an ENT Specialist: If you have ETD and need to use loud equipment, consult with an Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist to receive personalized advice and treatment options.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Keep track of any changes in your symptoms when exposed to loud noises or strong air currents and report them to your healthcare provider.
2. Environmental Considerations
Environmental factors play a significant role in managing ETD. Ensuring that you are in a controlled and supportive environment can help mitigate symptoms:
- Maintain Humidity Levels: Use a humidifier to keep your environment moist, which can help alleviate some ETD symptoms.
- Manage Allergies: Address any allergies that may contribute to ETD by using air purifiers and avoiding known allergens.
FAQs
1. Can using a leaf blower worsen Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
Yes, using a leaf blower can potentially worsen Eustachian Tube Dysfunction due to the high noise levels and strong air currents, which can aggravate ear pressure and discomfort.
2. What precautions should I take if I need to use a leaf blower with ETD?
If you must use a leaf blower, consider wearing ear protection, limiting exposure time, and maintaining a safe distance from the blower’s airflow to reduce discomfort.
3. Are there quieter alternatives to traditional leaf blowers?
Yes, there are quieter leaf blower models available that produce less noise. These may be a better option if you have ETD and are sensitive to loud sounds.
4. How can I manage ETD symptoms when exposed to loud noises?
To manage ETD symptoms, consult with an ENT specialist, use ear protection, monitor your symptoms, and consider environmental modifications like maintaining humidity and managing allergies.
5. What are some non-mechanical alternatives for yard maintenance?
Consider using manual tools such as rakes and brooms, which do not produce the noise or strong air currents associated with leaf blowers.
Conclusion
Navigating the use of a leaf blower with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction requires careful consideration of how noise and air pressure might impact your symptoms. While leaf blowers offer convenience for yard maintenance, they also present challenges for those with ETD. By understanding the potential effects and taking appropriate precautions, you can make informed decisions that help manage your condition effectively.
If you have ETD and need to use a leaf blower, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a strategy that minimizes discomfort and maintains your quality of life. Whether opting for quieter equipment or exploring alternative yard maintenance methods, the goal is to balance convenience with health considerations.